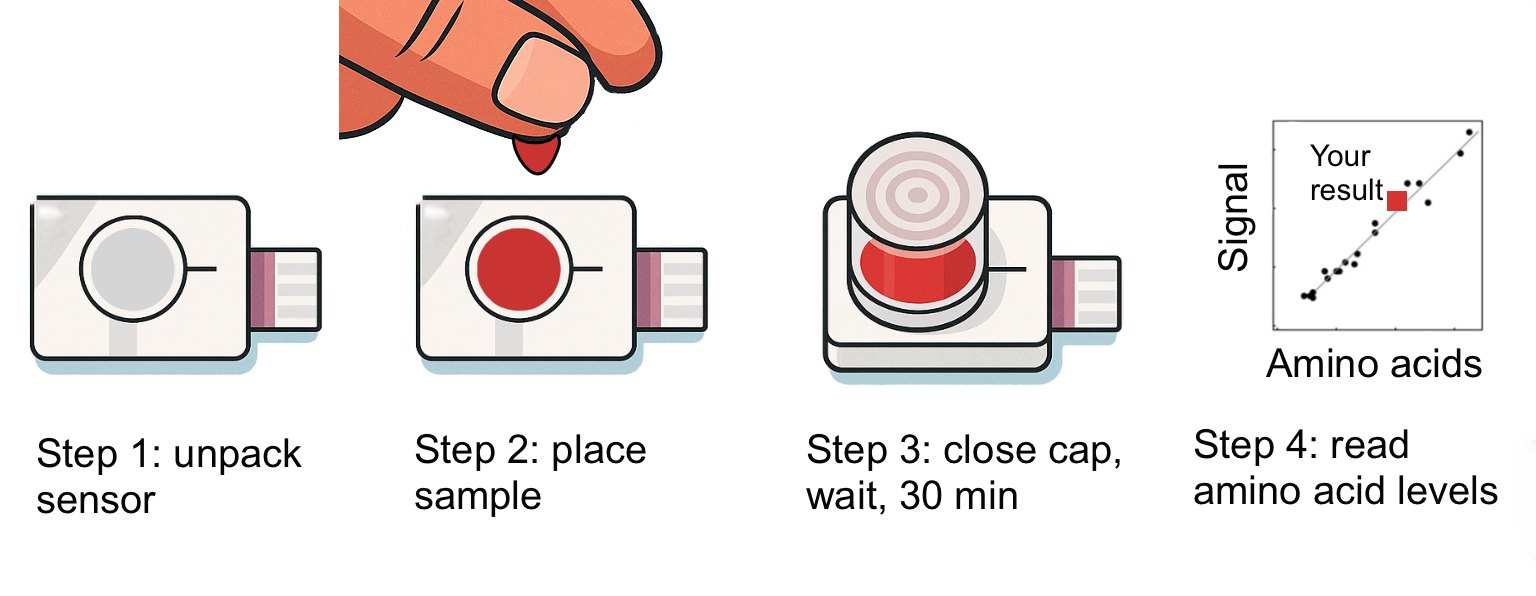
Point of care device – Aminometer – for rapid total L- amino acids measurement from a single drop of blood
Overview
The total pool of blood’s circulating L-amino acids (ΣAA) is an under-measured biomarker integrating muscle protein turnover, nutritional status or metabolic disorders. Despite its clinical relevance, current methods for quantifying ΣAA, including colorimetry and chromatography, are laboratory-bound, slow, and unsuitable for decentralized or extreme environments such as space missions. Contracted by European Space Agency, we are developing a portable, lightweight device – Aminometer – for rapid, calibration-free, convenient measurement of total L-amino acids (ΣAA) from a single drop of blood.
technical details
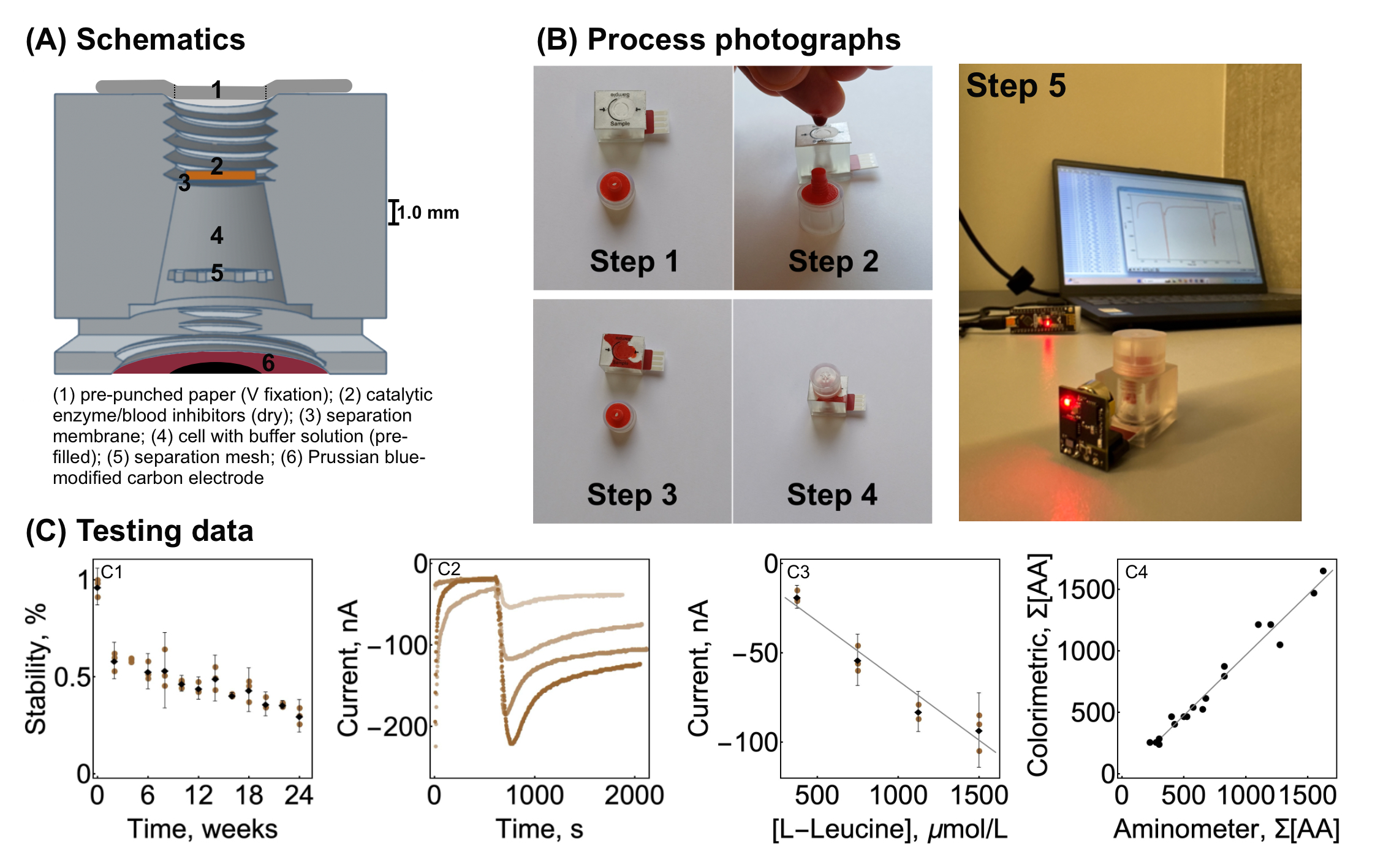
Paper-fixed 8.0 μL dosing and dried enzyme chemistry. A precut paper top fixes placed blood volume removing the need of external sampling devices (e.g. pipettes). (Figure 2)
Measurement parameters (for sensor chamber): limit of detection – 4.0 μM, limit of quantification – 6.4 μM, linear range – 15–60 μM (pre-calibrated against L-Leucine).
Measurement parameters (for blood sample): limit of detection – 100 μM, limit of quantification – 160 μM, linear range – 375–1500 μM (pre-calibrated against L-Leucine).
Full complete mass – 13 g, dimensions 34 × 19 × 26 mm with on-board battery.
Figure 2. A) Aminometer schematics – cross-section. (B) Process summary photographs involving finger prick sample placement (Step 1-4) and measurement (Step 5). (C) Testing data. C1 – Enzyme catalysts stability over 24 weeks. C2 – Current development curves for pre- calibration batch (from top to bottom: 375, 750, 1125 and 1500 μmol/L). C3 – Pre-calibration curve for concentration estimation. C4 – Validation data with model samples versus alternative colorimetric method.